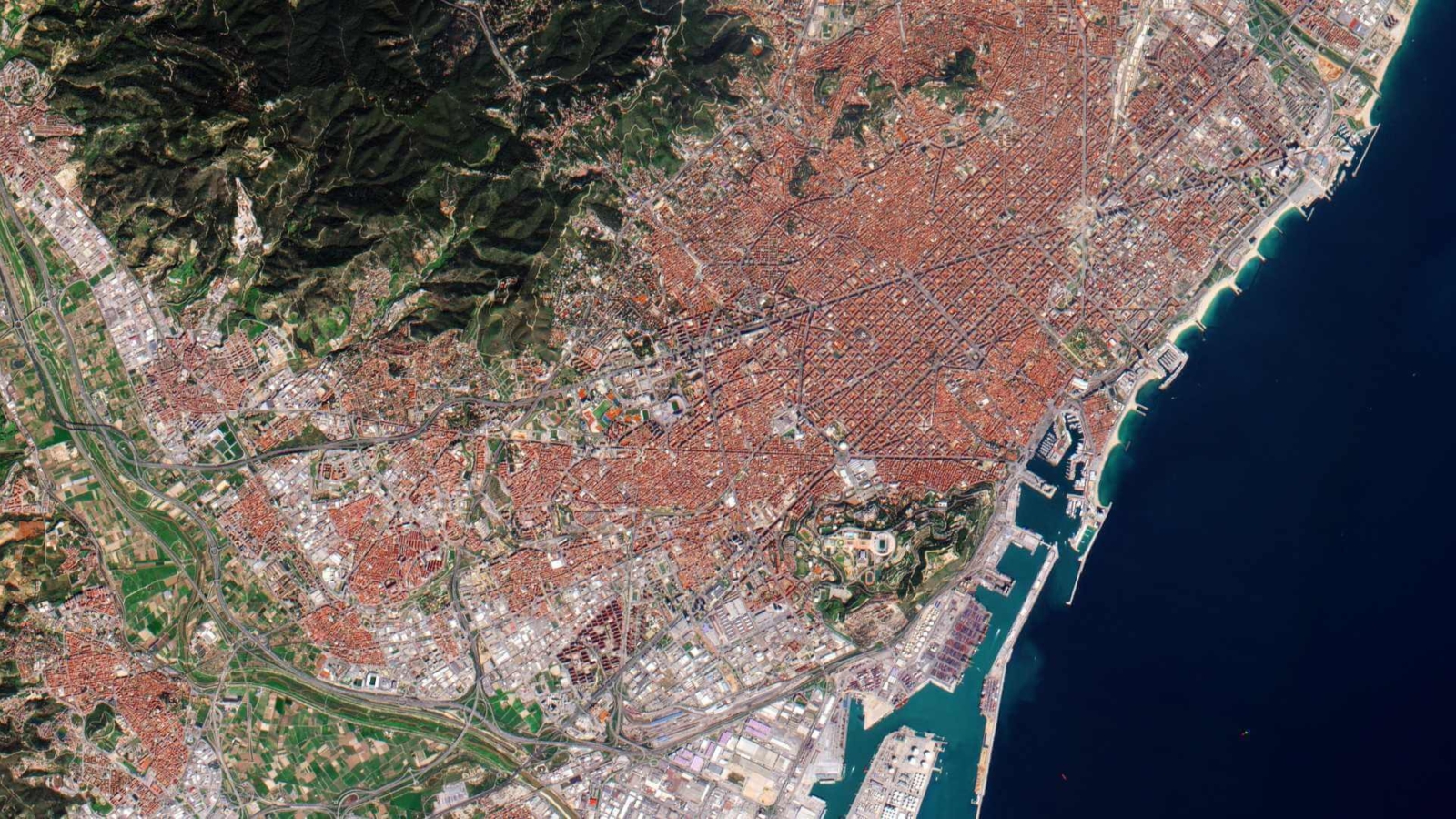
Landsat satellites have been orbiting Earth for nearly five decades, capturing invaluable data about our planet’s changing landscapes. From monitoring deforestation in the Amazon to tracking urban expansion in megacities, Landsat data plays a crucial role in understanding and managing Earth’s resources. As we delve into 2024, let’s explore the significance of Landsat data and its diverse applications across various domains.
Landsat, a joint program between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), has produced the longest continuous record of Earth’s surface observations from space. With a series of satellites launched since the program’s inception in 1972, Landsat has provided a wealth of multispectral imagery, covering every corner of the globe at a resolution suitable for detecting changes over time.
One of the primary applications of Landsat data is in land cover and land use mapping. By analyzing spectral signatures across different wavelengths, researchers can classify different types of land cover, such as forests, croplands, water bodies, and urban areas. This information is invaluable for land management, biodiversity conservation, and urban planning efforts worldwide.
Landsat data also plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental changes, including deforestation, desertification, and glacier retreat. Scientists leverage Landsat imagery to assess the extent and impact of these changes, helping policymakers develop strategies for mitigating environmental degradation and adapting to climate change.
Moreover, Landsat data is instrumental in agriculture, providing insights into crop health, yield estimation, and water management. By analyzing vegetation indices derived from Landsat imagery, farmers can optimize irrigation practices, detect pest infestations, and monitor crop growth throughout the growing season.
In addition to its scientific applications, Landsat data is also used for disaster response and recovery. During natural disasters such as wildfires, floods, and earthquakes, Landsat imagery provides valuable information for assessing the extent of damage, identifying vulnerable areas, and planning emergency response efforts.
Furthermore, Landsat data supports international initiatives such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), providing essential information for monitoring progress towards targets related to climate action, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable land management.
Looking ahead, the Landsat program is poised for continued innovation and expansion. With the launch of Landsat 9 in 2021, the program has entered a new era of advanced Earth observation capabilities, including improved spectral resolution and increased data continuity. These enhancements will further enhance the utility of Landsat data for a wide range of applications, from scientific research to commercial ventures.
In conclusion, Landsat data remains a cornerstone of Earth observation, providing a wealth of information about our planet’s changing surface. From land cover mapping to environmental monitoring, Landsat imagery supports a diverse array of applications with far-reaching implications for sustainable development and environmental stewardship. As we continue to harness the power of Landsat data, we unlock new insights into the dynamics of our ever-changing world.

